Abstract
Background. Anti-CD19 Chimeric Antigen Receptor (CAR) T-cells are a major therapeutic advance in the management of patients (pts) with relapsed/refractory aggressive B-cell lymphoma (R/R aggressive BCL) with reported overall response rates between 40% and 83% in the pivotal trials (ZUMA1, JULIET, TRANSCEND) as well as in the real-life cohorts with either axicabtagene ciloleucel (axi-cel, Yescarta) or tisagenlecleucel (tisa-cel, Kymriah). However, a significant number of pts will experience progression or relapse after infusion with an estimated 24-month progression-free survival (PFS) of between 33% and 42%. DESCAR-T is a nationwide registry that aims to collect real-life data for all pts treated with commercialized CAR T-cells in France. It represents a unique opportunity to investigate the outcome of pts who relapse after CAR T-cell therapy.
Patients and Methods. In all, 680 pts with R/R aggressive BCL were registered in DESCAR-T from August 2018 and 550 were infused at the time of the present analysis (April 12, 2021) with either axi-cel (n=350) or tisa-cel, n=200). All pts gave informed informed consent before DESCAR-T registration. Progression and relapse after CAR T-cells were defined based on the Cheson 2014 response assessment criteria.
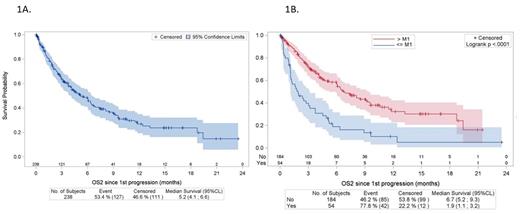
Results. With a median follow-up (F-up) of 7.9 months, 238 pts (43.3%) out of 550 treated pts relapsed, after axi-cel in 136 pts (F-up = 9.0 months [5.1 - 9.7]) and after tisa-cel in 102 pts (F-up = 7.8 months [5.9 - 10.4]). Histological subtypes were DLBCL (n 178, 74.8%), PMBL (n=11, 4.6%), HGBCL (n= 3, 1.3%), transformed follicular lymphoma (tr FL) (n=31, 13%), or other histologies (FL n=2, PCNSL n=1, tr MZL n=3, unclassifiable hodgkin/DLBCL n=9). At time of registration, median age was 62 years (range 18;77), 43.6% were aged >65 yrs, and 67.2% were male; 184 (79.7%) presented with advanced disease (stage III or IV), and 13 (5.9%) with low age-adjusted International Prognostic Index (aaIPI), 82 (37.1%) with low-intermediate aaIPI, 110 (49.8%) with high-intermediate aaIPI, and 16 (7.2%) with high aaIPI. At time of CAR T-cell infusion, 36 (18.9%) pts presented with ECOG PS >=2 and 72 (38.9%) with an elevated LDH level. The median number of lines prior to CAR T-cell infusion was 3 (range 2-9), including 48 (20.1%) transplant (46 auto-HSCT and 2 allo-HSCT). Median time between order and infusion was 50 days (IQR 43; 59). Bridging therapy was administered to 87.8% of the pts, with a high-dose regimen including combined immunochemotherapy for 84.5% of the pts. Failure after CAR T-cells occurred after a median time of 2.71 months (range 0.2; 21.5), 54 (22.7%) being during the first month after infusion (< M1) and 156 (65.5%) during the first-three months after infusion (<M3). At failure, 154 (64%) patients received treatments that maybe combined and described as followed : 70 (45.5%) lenalidomide, 70 (45.5%) various immunotherapies (rituximab, daratumomab, polatuzumab), 31 (20.1%) a combined immunochemotherapy with various regimens (R-DHAX, RICE, Pola-R-Benda,...), 21 (13.6%) an anti-PD1 immune checkpoint inhibitor (Nivolumab, pembrolizumab), 11 (7.1%) bi-specific T-cell engagers (TCE), 18 (11.7%) radiotherapy, and 3 a transplant (1 an auto-HSCT and 2 an allo-HSCT). The overall response rate to the salvage therapy after CAR T-cells was 11% (complete response rate 5.2%). The median PFS was 2.8 months (95% CL, 2.4 -3.1). The median overall survival (OS) was 5.2 months (95% CL, 4.1- 6.6) (Figure 1A). The median OS was even shorter in pts who failed during the first month (1.9 months [95% CL, 1.1- 3.2] vs 6.7 months [95 CL 5.5 : 9.3] p<0.0001) (Figure 1B). 26.9% of the pts in the overall cohort were alive at 6 months, but only 18.9% were alive in the group of pts relapsing during the first month. In multivariate analysis, predictors of OS were high LDH level at time of infusion, time to failure < 1 month after CAR T-cells, no access to immuno-oncology treatment such as TCE or lenalidomide.
Conclusion. This study is the first analysis reporting the outcome of patients with R/R aggressive BCL relapsing after anti-CD19 CAR T-cells. These results demonstrate the poor outcome of these pts and identifies the need for further innovative treatment strategies.
Figure1. Overall survival from the CAR T-cell infusion in patients with R/R LBCL relapsing after CAR T-cells. (A) overall population. (B) according to the interval between CAR T-infusion and relapse (< 1 month and > 1 month)
Di Blasi: Novartis: Consultancy, Honoraria; Kite, a Gilead Company: Consultancy, Honoraria; Janssen: Consultancy, Honoraria. Bachy: Kite, a Gilead Company: Honoraria; Novartis: Honoraria; Daiishi: Research Funding; Roche: Consultancy; Takeda: Consultancy; Incyte: Consultancy. Cartron: Roche, Celgene-BMS: Consultancy; Danofi, Gilead, Novartis, Jansen, Roche, Celgene-BMS, Abbvie, Takeda: Honoraria. Le Bras: Takeda: Honoraria, Research Funding; Kite Gilead: Honoraria; Novartis: Honoraria; Celgene BMS: Research Funding. Feugier: Janssen: Consultancy, Honoraria; Gilead: Consultancy, Honoraria; Abbvie: Consultancy, Honoraria; Amgen: Honoraria; Astrazeneca: Consultancy, Honoraria. Casasnovas: Roche: Consultancy, Honoraria, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Research Funding; Takeda: Consultancy, Honoraria, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Research Funding; Gilead Kite: Consultancy, Honoraria, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Research Funding; MSD: Consultancy, Honoraria, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; BMS: Consultancy, Honoraria, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Amgen: Consultancy, Honoraria; Janssen: Consultancy, Honoraria; Abbvie: Consultancy, Honoraria. Mohty: Amgen: Honoraria; Jazz: Honoraria, Research Funding; Sanofi: Honoraria, Research Funding; Pfizer: Honoraria; Novartis: Honoraria; Takeda: Honoraria; Janssen: Honoraria, Research Funding; Gilead: Honoraria; Celgene: Honoraria, Research Funding; Bristol Myers Squibb: Honoraria; Astellas: Honoraria; Adaptive Biotechnologies: Honoraria. Sesques: Kite, a Gilead Company: Honoraria; Novartis: Honoraria; Chugai: Honoraria. Morschhauser: Servier: Consultancy; Incyte: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Chugai: Honoraria; AbbVie: Consultancy, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Genmab: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Novartis: Consultancy, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Gilead: Consultancy, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; AstraZenenca: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Epizyme: Consultancy, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Roche: Consultancy, Speakers Bureau; F. Hoffmann-La Roche Ltd: Consultancy, Honoraria, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Genentech, Inc.: Consultancy; BMS: Consultancy, Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Janssen: Honoraria; Celgene: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees.